What is a managed SIEM service?
SIEM technology is a combination of security event management (SEM) and security information management (SIM) technologies. It allows organizations to continuously monitor their on-premise and cloud IT infrastructure for threats and to provide the information needed to respond to attacks and to mitigate vulnerabilities.
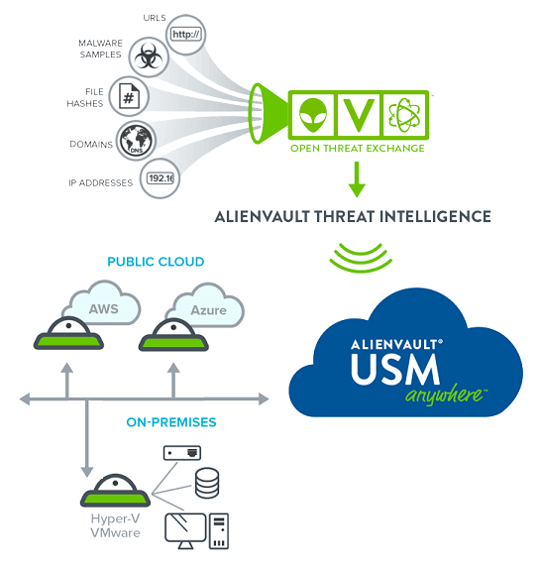
CommSec has partnered with AlienVault to provide a world class managed Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) service organisations of all kinds in the Irish market.
AT&T CyberSecurity (AlienVault) SIEM technology collects logs and events from IT systems, devices and networks. We use this data to detect, categorize and analyse security incidents. The SIEM monitors threats in real-time and correlates events against the Open Threat Exchange (OTX – the world’s most authoritative open threat information sharing and analysis network).
What is a firewall?
A Firewall is a network security device that monitors, and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on an organization’s previously established security policies. At its most basic, a firewall is essentially the barrier that sits between a private internal network and the public Internet.
Network firewalls are evolving to secure newer use cases, including cloud and sudden shift to growing remote workforce. Network firewalls can also offer additional capabilities, such as application awareness and control, intrusion detection and prevention, advanced malware detection, and logging and reporting.
We can install, configure, manage and support your firewall, whether on-premise or in the cloud. We deliver our resources, our expertise and our best in class change management, incident investigation and response management and integrated vendor support processes to ensure a fully effective firewall service protecting your network and services.
How Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) Work
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are both parts of the network infrastructure. IDS/IPS compare network packets to a cyberthreat database containing known signatures of cyberattacks — and flag any matching packets.
What is Anti-Malware?
An anti-malware is a software that protects the computer from malware such as spyware, adware, and worms. It scans the system for all types of malicious software that manage to reach the computer. An anti-malware program is one of the best tools to keep the computer and personal information protected.
An anti-malware is designed to eliminate malware from the computer. Although it has similarities with antivirus, an anti-malware program is different from antivirus. An anti-malware program has more advanced features and broader coverage. It addresses spyware, spam, and other threat issues that antivirus doesn’t.
What is vulnerability management?
Every year, thousands of new vulnerabilities are discovered, requiring organisations to patch operating systems (OS) and applications and reconfigure security settings throughout the entirety of their network environment. To proactively address vulnerabilities before they are utilised for a cyberattack, organisations serious about the security of their environment perform vulnerability management to provide the highest levels of security posture possible.
Vulnerability management is generally defined as the process of identifying, categorising, prioritising, and resolving vulnerabilities in operating systems (OS), enterprise applications (whether in the cloud or on-premises), browsers, and end-user applications. An ongoing process, vulnerability management seeks to continually identify vulnerabilities that can be remediated through patching and configuration of security settings.
What is identity and access management?
Identity and access management (IAM) is a framework of business processes, policies and technologies that facilitates the management of electronic or digital identities. With an IAM framework in place, information technology (IT) managers can control user access to critical information within their organizations. Systems used for IAM include single sign-on systems, two-factor authentication, multifactor authentication and privileged access management. These technologies also provide the ability to securely store identity and profile data as well as data governance functions to ensure that only data that is necessary and relevant is shared.
IAM systems can be deployed on premises, provided by a third-party vendor through a cloud-based subscription model or deployed in a hybrid model.
On a fundamental level, IAM encompasses the following components:
- how individuals are identified in a system (understand the difference between identity management and authentication);
- how roles are identified in a system and how they are assigned to individuals;
- adding, removing and updating individuals and their roles in a system;
- assigning levels of access to individuals or groups of individuals; and
- protecting the sensitive data within the system and securing the system itself.





