NIS2 Directive Origins
The original Network and Information Security Systems Directive (NIS1) was introduced to enhance the cyber security of Europe’s essential services. Over time, the growing frequency and impact of cyber-attacks, particularly on critical infrastructure, highlighted the need for stronger measures. This led to the introduction of NIS2, which builds on the foundation of NIS1 to address emerging threats and challenges.
EU member states were required to incorporate NIS2 into their national laws by 17 October 2024, with the new regulations coming into force on 18 October 2024, replacing the original NIS Directive. While some member states have met this deadline, others are expected to implement NIS2 sometime in 2025, including Ireland.
NIS2 Directive Scope
Entities are brought into scope of the NIS2 Directive based on their size and importance:
- Medium-sized organisations: 50+ employees or €10 million+ annual turnover/balance sheet total.
- Large organisations: 250+ employees or €50 million+ annual turnover or €43 million+ balance sheet total.
- Exceptions: Smaller entities may be included if they play a critical role in essential sectors like energy, transport, and health.
This ensures minimum levels of cyber resilience for critical sectors across Europe and Ireland.
Check to see if you're in scopeFines, Penalities and Sanctions under NIS2
Under the NIS2 Directive, organisations that fail to comply with cybersecurity requirements face significant penalties:
- Fines: Up to €10 million or 2% of the global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
- Sanctions: May include orders to implement corrective measures, suspension of operations, or public disclosure of non-compliance.
- Penalties: Applied for failure to meet the required security measures, incident reporting, or cooperation with authorities.
These penalties aim to enforce strict compliance and enhance cybersecurity across essential and important sectors.
nis2 Sectors in scope
The NIS2 Directive applies to a broad range of sectors and industries, classified into two main groups: Essential Entities and Important Entities. Below are the sectors and industries in scope:
Essential Entities:
- Energy: Electricity, including production, transmission, and distribution. Oil, including production, refining, distribution, and storage.Gas, including transmission, distribution, storage, and supply.
- Transport: Air transport, including airlines, airports, and air navigation services. Rail transport, including infrastructure and operators. Water transport, including maritime ports, shipping, and inland waterways. Road transport, including operators of road infrastructure and passenger services.
- Banking: Credit institutions, including banks.
- Financial Market Infrastructures: Trading venues, central counterparties, and central securities depositories.
- Health: Healthcare providers, including hospitals, private clinics, and telemedicine services. Digital infrastructure, such as data centers, cloud computing services, and content delivery networks.
- Drinking Water Supply and Distribution: Providers of potable water.
- Wastewater: Wastewater collection, treatment, and disposal services.
- Digital Infrastructure: DNS service providers, TLD name registries, cloud computing service providers, data centers, and content delivery networks.
- Public Administration: Public entities at central and regional levels that provide essential services to the public.
These sectors are considered critical to the economy, society, and public safety, and the NIS2 Directive aims to enhance the cybersecurity resilience of entities operating within them.
Important Entities:
- Postal and Courier Services: Services related to postal delivery and courier activities.
- Waste Management: Providers of waste collection, treatment, and disposal services.
- Chemical Industry: Production, storage, and distribution of chemicals.
- Food Production, Processing, and Distribution: Includes large-scale food production and processing facilities.
- Manufacturing: Manufacture of medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and other critical products.
- Space: Providers of services related to space operations, such as satellite services.
- Research & Development in Critical Technologies: Entities involved in research and development in sectors crucial for national security and public safety.
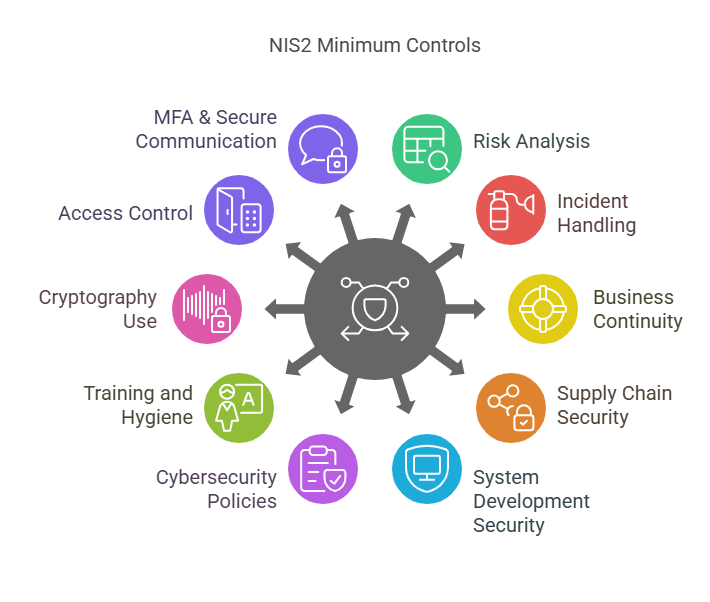
Nis2 10 minimum controls
These miniumum controls are essential for organisations to manage cyber security risks effectively, ensuring resilience against potential cyber threats
- Risk analysis & information system security
- Incident handling
- Business continuity measures (back-ups, disaster recovery, crisis management)
- Supply Chain Security
- Security in system acquisition, development and maintenance, including
vulnerability handling and disclosure - Policies and procedures to assess the effectiveness of cybersecurity risk management measures
- Basic computer hygiene and trainings
- Policies on appropriate use of cryptography and encryption
- Human resources security, access control policies and asset management
- Use of multi-factor, secured voice/video/text comm & secured emergency
communication
(Source: NCSC Quick Reference Guide).
How can CommSec Help with NIS2?
Unlock Compliance with Expert Guidance
Start your compliance journey with a tailored consultancy service. At CommSec, we take a consultancy-led approach to ensure your organisation meets all NIS2 obligations. Every compliance requirement is unique, requiring thorough investigation and scoping.
Our process begins with a comprehensive gap analysis to identify your current standing. From there, we work closely with you to bridge those gaps, providing expert advice and helping you select world-class tools to achieve full compliance.
Get in Touch Today to Discuss Your Requirements and Take the First Step Towards NIS2 Compliance.


