As the year draws to a close, our cybersecurity team reflects on a period marked by escalating cyber threats, innovative attacks, and a heightened sense of vigilance. While 2023 brought its share of challenges, it also reinforced the importance of robust cybersecurity measures and the dedication of our frontline experts in safeguarding our customers’ critical data and systems.
One of the most notable incidents of the year was the social engineering attack that crippled a Las Vegas casino, MGM and highlighting the inherent vulnerability of human interaction to manipulation.
The biggest breach in terms of reach was The MoveIT supply chain attack, which compromised thousands of businesses and exposed millions of individuals’ data, underscores the interconnectedness of modern IT ecosystems and the potential for widespread disruption through a single compromised link.
Hacktivism, both globally and at home, served as a stark reminder of the political and ideological motives that drive cyber adversaries. Recently an attack launched by hackers against the systems of a small water utility in Ireland interrupted the water supply for two days. It was reported that the hackers targeted a Eurotronics water pumping system, defacing a user interface with a message announcing the hack. The hackers also posted an anti-Israel message and said they targeted the system due to it being made in Israel. Many hackers joined in on the Israel-Hamas war immediately after the conflict escalated in early October.
In this blog post, we delve into these significant events, seeking to extract lessons learned, identify emerging trends, and assess the future of cybersecurity. Our frontline cybersecurity people share their insights, providing valuable perspectives on the evolving threat landscape and the measures we must implement to stay ahead of the curve.
The Top Cyber Security Trends in 2023
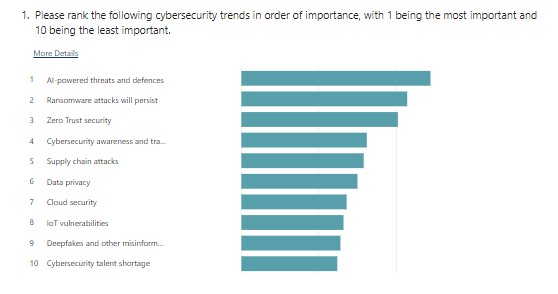
AI-powered threats
AI-powered threats are defined as, threat actors who can use AI to create advanced malware, impersonate others for scams, and poison AI training data. They can use AI to automate phishing, malware, and credential-stuffing attacks (source). The use cases seem endless for AI-powered threats and that is why we believe it deserves the top spot.
There has been plenty of fuss/hype around AI-powered threats in 2023 and you would be forgiven for being dismissive about the reality of the threats. However, despite drawing debate about the scale of use, AI threats have been around for many years now. For example, in 2015, hackers used an AI-powered malware called BlackEnergy to attack power grids in Ukraine, causing widespread blackouts and disruption to the country’s energy supply. In another example, a UK energy firm was scammed out of £200,000 in 2019 when a hacker used AI to impersonate a CEO’s voice in a phone call.
How do you defend against these threats, well you just have to fight AI with AI. Just like AI threats, cyber Security tools have been using machine learning for years to help detect, analyse, and respond to threats.
AI-powered cybersecurity revolutionises threat detection and response, surpassing traditional software-driven approaches. AI-driven threat detection systems can recognize patterns of behaviour that human analysts might miss. This proactive approach to cybersecurity can significantly reduce response times and limit the damage caused by AI-driven attacks (source).
AI-powered cybersecurity is like having a super-smart security system that can find and stop threats faster than regular systems. It can quickly look at millions of events and spot different threats. It can also learn from this data to understand what’s normal and what’s not. This means it can spot things that are wrong even if it’s never seen them before. AI systems can also learn from billions of pieces of data to get a better understanding of how threats work and how to stop them. This means they can be more accurate at detecting attacks and can prioritise the most important ones to fix.
Overall, AI-powered cybersecurity is a powerful tool that can help organisations protect themselves from the ever-growing number of cyber threats.
Ransomware
Ransomware has been a top attack method for the past decade, and to is not going away anytime soon, because if something works, hackers will keep using it until it is no longer profitable. Phishing campaigns are still the most common way to get ransomware into a system, according to the latest report from Sophos in their 2023 Adversary Report:
- Compromised credentials are now the #1 root cause of incidents.
- RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) plays a part in 95% of attacks.
- Ransomware dwell time has almost halved since 2022.
- 90% of ransomware attacks occur outside standard weekday business hours (i.e., outside 8 am – 6 pm, Monday – Friday).
- It takes less than a day for attackers to reach Active Directory.
Another trend of note is that Ransomware may be changing where the Malware element of ransomware is not deployed meaning the hackers just take the data and encrypt it, then demand payment or ransom for its release or threaten to publish it on the web.
Social Engineering
The MGM ransomware and social engineering attack dominated headlines and Google searches in 2023. In early September, the casino and hotel chain reported a “cyber security issue” that led to a 10-day system shutdown. The effects were felt throughout the Las Vegas strip, with offline gambling machines and disabled electronic hotel keys disrupting the fun times of vacation goers. Most importantly, the hackers claim to have stolen 6 terabytes of data, including social security numbers. MGM is said to have lost $80 million in revenue from the shutdown. This ransomware attack occurred because of a social engineering technique used on the IT Help Desk. The question is, did the MGM provide cybersecurity awareness training for the IT helpdesk? If so, would it have helped avoid the ransomware attack?
Zero Trust
Zero Trust principals have come to the forefront of cybersecurity thinking in the last couple of years. The simple way to look at Zero Trust is to trust nothing and no one – a human, a device or an IP address for example. Zero Trust is now the backbone of modern-day cyber security strategy and emerging technologies like SASE and next-generation firewalls underpin the ideology and allow for safe working whether remotely or on-premise.
MoveIT Attack
The MoveIT supply chain attack is seen as the biggest hack of 2023 and affected hundreds of blue-chip organisations including British Airways, Aer Lingus, Sony, and Boots. An attack emanated from the Cl0p ransomware Group exploiting a vulnerability in Progress Software’s MoveIT file transfer platform. The breach exposed sensitive personal data belonging to approximately 62 million people. This type of breach highlights the importance of not only securing your supply chain but also the supply chain of your vendors and suppliers that are digitally connected to your organisation. Supply chain audits are becoming more common as we encounter these supply chain attacks and are driven by requirements from international cyber security standards such as NIS2 and DORA to encourage supply chain risk assessment and hygiene measures.
Cyber Security Awareness Training
Cyber Security Awareness Training (SAT) has grown in popularity in recent years and provides organisations with a “prevention is better than the cure” approach to cyber security. Education no matter what form it takes is only positive on the impact of personal development and in this case, gives employees a baseline of understanding of the common threats out there. To make the SAT a success organisations need to take a programmed approach and provide regular training with quizzes and progression levels to reinforce learning. Another factor is SAT training can now take an industry or job-related content-focus making it even more effective. Adding a phishing campaign element to the training has become the norm to evaluate the effectiveness of the training.
Uncertain about your cyber security posture? Consult our experts today. We are here to provide clear, independent guidance and answer all your questions. Contact us here.









